Understanding Solar System Connection Types
When choosing a solar energy system, one of the most important decisions is whether to go for an off-grid or on-grid setup. Both systems generate electricity from sunlight, but the way they store, use, and distribute power is very different. Understanding these differences helps you choose a system that matches your location, budget, and energy needs.
What an On-Grid Solar System Means
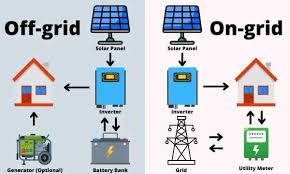
An on-grid solar system is connected directly to the national electricity grid. During the day, solar panels supply electricity to your home or business, reducing the amount of power you draw from the grid. When solar production is low or unavailable, the grid automatically supplies electricity to make up the difference. Because batteries are usually not required, on-grid systems are generally cheaper to install.
Advantages of On-Grid Solar Systems
On-grid systems are popular in areas where public electricity is relatively stable. They reduce monthly electricity bills and make efficient use of solar power without the high cost of battery storage. In regions where net metering is available, excess electricity generated during the day can be sent back to the grid, further increasing savings.
Limitations of On-Grid Solar Systems
The biggest limitation of an on-grid system is that it shuts down during power outages. For safety reasons, the system stops supplying electricity when the grid goes off. This means that even if the sun is shining, you may still experience blackout periods unless you have an additional backup solution.
What an Off-Grid Solar System Means
An off-grid solar system operates completely independently from the national grid. All the electricity generated is stored in batteries and used as needed. This type of system is designed to supply power at all times, regardless of whether public electricity is available or not.
Advantages of Off-Grid Solar Systems
Off-grid systems provide full energy independence and are ideal for areas without grid access or with extremely unreliable power supply. They ensure continuous electricity for homes, farms, and businesses in remote locations. Once installed properly, off-grid systems remove the need for fuel-powered generators entirely.
Challenges of Off-Grid Solar Systems
Because off-grid systems rely heavily on batteries, the installation cost is higher. Battery storage must be carefully sized to handle night-time usage and cloudy days. Poor system design or underestimating energy consumption can lead to power shortages.
Cost Comparison Between Off-Grid and On-Grid Systems
On-grid systems have lower upfront costs because they do not require large battery banks. Off-grid systems are more expensive initially due to batteries and larger system capacity, but they offer complete independence from electricity tariffs and outages. Over time, the value of reliable power often outweighs the higher installation cost.
Which Solar System Is Best for You?
The best system depends on your electricity situation. If you live in an area with stable grid power and want to reduce electricity bills, an on-grid system may be sufficient. If you experience frequent blackouts or have no access to public electricity, an off-grid system is a better long-term solution. In many cases, a hybrid system offers a balance between both options.
Final Thoughts on Choosing the Right Solar System
Both off-grid and on-grid solar systems have their place. The right choice comes down to reliability, budget, and energy needs. By understanding how each system works and what it offers, you can invest in a solar solution that delivers consistent power and long-term savings.







Leave a Reply