What a Solar Inverter Does in a Solar System
A solar inverter is the heart of any solar power system. Solar panels produce direct current electricity, but most home and business appliances use alternating current. The inverter’s job is to convert this electricity into a usable form. Without an inverter, solar power generated by panels cannot run everyday appliances.
Why Choosing the Right Inverter Matters
The inverter determines how efficiently your solar system performs. A poor-quality or undersized inverter can lead to frequent system shutdowns, reduced battery life, and damaged appliances. Choosing the correct inverter type ensures stable power, system safety, and long-term reliability.
String Inverters Explained
String inverters are the most commonly used inverter type in residential solar systems. In this setup, multiple solar panels are connected in series to a single inverter. The inverter manages the entire panel array as one unit, converting all the generated electricity at once. This type is affordable and works well in locations where panels receive uniform sunlight.
Limitations of String Inverters
When one panel in a string is shaded or underperforming, the output of the entire system can drop. This makes string inverters less ideal for rooftops with shading issues or panels facing different directions.
Microinverters Explained
Microinverters are small inverters installed on each individual solar panel. Each panel operates independently, converting electricity at the panel level. This allows the system to perform better in shaded or uneven sunlight conditions and provides more detailed performance monitoring.
When Microinverters Are a Better Choice
Microinverters are ideal for complex rooftops, partial shading, or systems where maximum efficiency is required. Although they cost more upfront, they often deliver higher energy output over time.
Hybrid Inverters Explained
Hybrid inverters combine the functions of a solar inverter and battery inverter in one unit. They manage solar panels, batteries, and grid electricity simultaneously. This makes them a popular choice in areas with unstable grid power because they allow energy storage and backup power.
Benefits of Hybrid Inverters
Hybrid inverters provide flexibility and energy security. They allow users to store excess solar power in batteries and switch automatically between solar, battery, and grid power when needed. This results in improved reliability and better energy control.
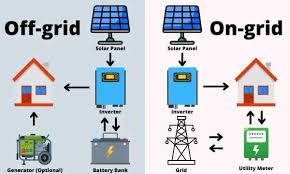
Off-Grid Inverters Explained
Off-grid inverters are designed for systems that operate independently from the national grid. They work with large battery banks and supply power at all times without relying on public electricity. These inverters are common in rural and remote locations.
Pure Sine Wave vs Modified Sine Wave Inverters
Pure sine wave inverters produce clean electricity that is safe for all appliances, including sensitive electronics. Modified sine wave inverters are cheaper but may cause noise, overheating, or reduced lifespan in certain appliances. For most modern homes and businesses, pure sine wave inverters are the better option.
How to Choose the Right Solar Inverter
Choosing the right inverter depends on your power usage, system size, grid availability, and budget. A properly sized inverter with good surge capacity ensures smooth operation and system longevity.
Final Thoughts on Solar Inverters
Solar inverters play a critical role in system performance and reliability. Understanding the different inverter types helps beginners make informed decisions and avoid costly mistakes. With the right inverter, a solar energy system can deliver stable, efficient, and long-lasting power.







Leave a Reply